Scatter Plot Maker Scatter Plots
Describe your data and variables, and our AI will create a professional scatter plot instantly. Perfect for research papers, data analysis, and academic presentations.
Scatter Plot Generator
Free to try ·
Your scatter plot will appear here
Describe your data and click Generate
Scatter Plot Examples
Browse examples from different research fields or generate your own above
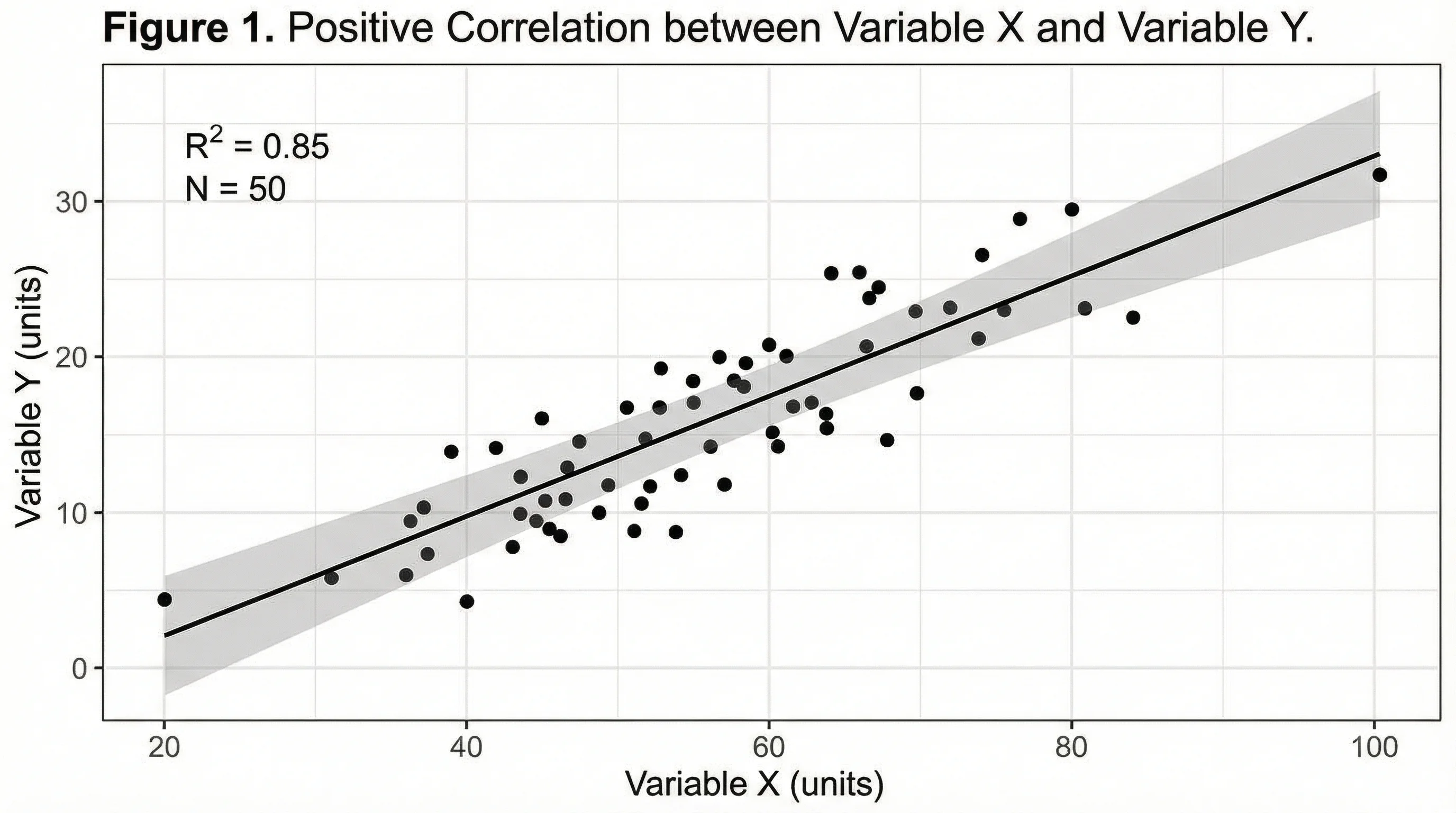
Positive Correlation Study
Classic positive correlation scatter plot with trend line, ideal for demonstrating linear relationships in educational research.
Multi-Group Comparison
Multi-group scatter plot showing treatment comparisons across clinical study groups with individual trend lines.
Regression Analysis
Regression analysis scatter plot with confidence intervals, perfect for scientific publications.
Climate Data Visualization
Geographic research scatter plot comparing climate variables across continents with color-coded data points.
Student Performance Analysis
Educational research scatter plot analyzing cross-subject student performance with quadrant analysis.
Enzyme Kinetics Data
Biochemistry scatter plot with error bars and curve fitting for enzyme kinetics analysis.
4 more examples available
Sign in for free to unlock all example diagrams and generate your own 4k custom diagrams.
What is a Scatter Plot?
A scatter plot (also called a scatter diagram or scatter graph) is a type of data visualization that uses Cartesian coordinates to display values for two variables. Each data point is represented as a dot positioned according to its values on the x-axis and y-axis. Scatter plots are one of the most fundamental tools in statistical analysis, allowing researchers to visually identify relationships, patterns, and outliers in their data. They are widely used across scientific disciplines, from biology and medicine to economics and engineering.
When to Use Scatter Plots in Research
- Exploring relationships between two continuous variables before running formal statistical tests
- Identifying positive, negative, or non-linear correlations between research variables
- Detecting outliers and anomalous data points that may affect analysis results
- Comparing multiple groups or treatment conditions on two measured outcomes
- Presenting regression analysis results with trend lines and confidence intervals
- Visualizing large datasets to communicate patterns clearly in publications and presentations
How to Interpret Scatter Plot Patterns
Understanding scatter plot patterns is essential for data analysis. A positive correlation shows data points trending upward from left to right, indicating that as one variable increases, the other tends to increase as well. A negative correlation shows a downward trend, meaning the variables move in opposite directions. No correlation appears as a random cloud of points with no discernible pattern. Non-linear relationships may show curved patterns such as quadratic, exponential, or logarithmic trends. The strength of correlation can be assessed by how tightly the points cluster around the trend line, with R-squared values quantifying the proportion of variance explained.
Scatter Plot Best Practices for Academic Papers
- Label both axes clearly with variable names and units of measurement
- Include a descriptive title or caption that explains what the plot shows
- Add trend lines with equations and R-squared values when reporting correlations
- Use different colors or markers for multiple groups and include a legend
- Show error bars when presenting averaged or aggregated data points
- Choose appropriate axis scales that do not exaggerate or minimize relationships
Common Mistakes in Scatter Plot Design
Researchers frequently make avoidable errors when creating scatter plots. Overcrowding the plot with too many data points without adjusting transparency makes patterns invisible. Using inappropriate axis scales can exaggerate weak correlations or hide strong ones. Fitting linear trend lines to clearly non-linear data misrepresents the relationship. Omitting confidence intervals gives a false sense of certainty. Ignoring outliers without justification can bias regression results. Our AI scatter plot maker helps you avoid these pitfalls by generating publication-ready visualizations that follow best practices in data presentation.
Frequently Asked Questions
More Data Visualization Tools
 Visualization
VisualizationAI Chart Generator
Create professional charts including bar charts, line graphs, pie charts, and more for data visualization.
 Research
ResearchConceptual Framework Generator
Create professional conceptual frameworks to visualize research variables and their relationships.
 Research
ResearchAI Scientific Image Generator
Generate scientific illustrations, diagrams, and figures for research papers and educational materials.