Network Diagram Generator Network Diagrams
Describe your network infrastructure and our AI will create professional topology diagrams with standard networking symbols. Perfect for IT planning, cloud architecture, and security documentation.
Network Diagram Generator
Free to try ·
Your network diagram will appear here
Describe your network and click Generate
Network Diagram Examples
Browse IT infrastructure examples or generate your own above
Enterprise Network Topology
Professional enterprise network topology diagram with LAN/WAN segments, core and distribution switches, routers, firewalls, DMZ servers, and workstations with labeled subnets and VLANs.
Cloud Infrastructure Architecture
AWS-style cloud architecture diagram featuring load balancer, auto-scaling web servers, application tier, RDS database with read replica, S3 storage, and CloudFront CDN within a VPC.
Home Network Setup
Simple home network diagram illustrating ISP connection to modem, wireless router, and various connected devices including laptop, desktop, smart TV, smartphone, printer, and IoT devices.
Data Center Spine-Leaf Architecture
Data center network diagram featuring spine-leaf architecture with spine switches connecting to leaf switches, server racks, storage arrays, and out-of-band management network.
Wireless Network Coverage Plan
Wireless network planning diagram with building floor plan, multiple access points with overlapping coverage zones, PoE switches, WLAN controller, and channel assignments.
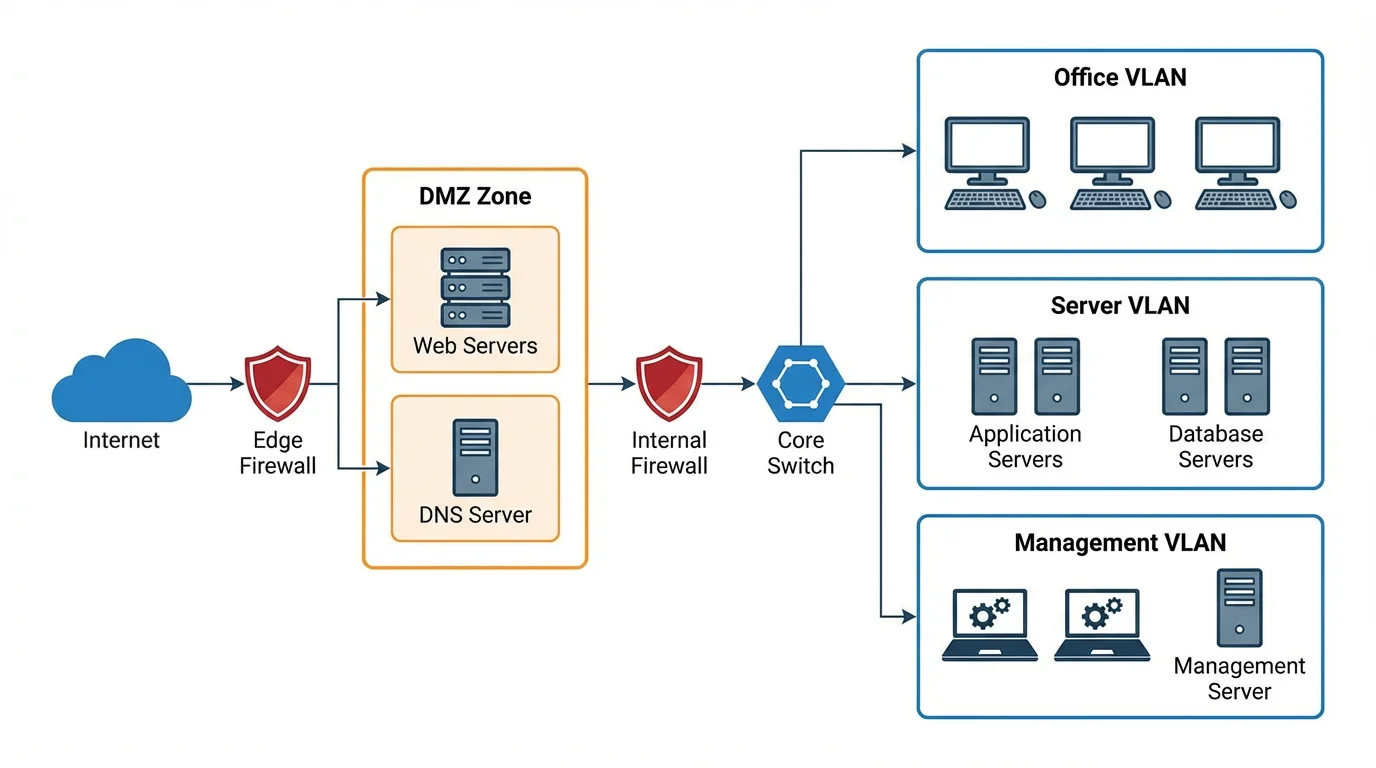
Network Security Architecture
Defense-in-depth network security diagram with external firewall, DMZ, internal firewall, IDS/IPS system, segmented internal networks, VPN gateway, and SIEM system.
4 more examples available
Sign in for free to unlock all example diagrams and generate your own 4k custom diagrams.
What Is a Network Diagram?
A network diagram is a visual representation of a computer network that shows the arrangement of devices, connections, and communication paths within an infrastructure. Network diagrams map out how routers, switches, firewalls, servers, and endpoints are interconnected, making them essential for IT planning, troubleshooting, and documentation. From simple home networks to complex enterprise data centers, these diagrams provide a clear overview of network topology that helps engineers understand data flow, identify single points of failure, and plan capacity upgrades.
Types of Network Topologies
- Star Topology: All devices connect to a central hub or switch, simple to manage but creates a single point of failure at the center
- Bus Topology: All devices share a single communication line, cost-effective for small networks but prone to collisions and limited scalability
- Ring Topology: Devices form a closed loop where data travels in one direction, providing predictable performance but disrupted if any node fails
- Mesh Topology: Every device connects to every other device, providing maximum redundancy and reliability for mission-critical networks
- Hybrid Topology: Combines two or more topologies (e.g., star-bus or star-ring) to balance cost, performance, and reliability for real-world deployments
- Spine-Leaf Topology: Modern data center design with spine switches connecting to leaf switches, providing equal-cost paths and predictable latency
Network Diagram Symbols and Conventions
Standard network diagrams use established symbols for clarity and consistency. Routers are represented by circles with arrows, switches by rectangles with bidirectional arrows, firewalls by brick wall icons, servers by tower/rack icons, and workstations by monitor icons. Cloud shapes represent the internet or external networks, while dashed lines indicate wireless connections and solid lines represent wired links. Color coding distinguishes network segments: green for internal trusted networks, red for external untrusted zones, and orange for DMZ areas. Following these conventions ensures your diagrams are immediately understandable by any IT professional.
When to Use Network Diagrams
Network diagrams are critical during infrastructure planning to design new deployments and validate that connectivity requirements are met before purchasing equipment. During troubleshooting, they help engineers quickly trace the path of failed connections and identify where bottlenecks occur. For security audits, network diagrams reveal the attack surface, firewall placement, and segmentation boundaries. Compliance frameworks like PCI-DSS, HIPAA, and SOC 2 often require up-to-date network documentation. Cloud migration projects rely on network diagrams to map existing on-premise infrastructure to equivalent cloud VPC, subnet, and security group configurations.
Network Diagram Best Practices for IT Teams
- Layer your diagrams: create separate physical, logical, and security views rather than cramming everything into one diagram
- Label all connections with bandwidth, protocol, and VLAN information so engineers can assess capacity at a glance
- Include IP addressing schemes, subnet masks, and gateway information for each network segment
- Use consistent iconography following industry standards (Cisco, AWS, or ISO 7498) across all documentation
- Keep diagrams version-controlled and update them whenever changes are made to the infrastructure
- Add a legend explaining custom symbols, color codes, and abbreviations used in the diagram
Frequently Asked Questions
More Diagram Tools
 Diagrams
DiagramsText to Diagram Generator
Convert text descriptions into structured diagrams including flowcharts, architecture diagrams, and more.
 Diagrams
DiagramsAI Flowchart Generator
Create professional flowcharts for processes, decision trees, and workflows with AI assistance.
 Research
ResearchMind Map Generator
Organize ideas and concepts visually with AI-generated mind maps for brainstorming and planning.